The import of CRM data from Salesforce into Fullcast is controlled by the configuration of entities and fields. This is where you can control which objects and fields are imported into Fullcast. The import process is the same for all standard integrations.
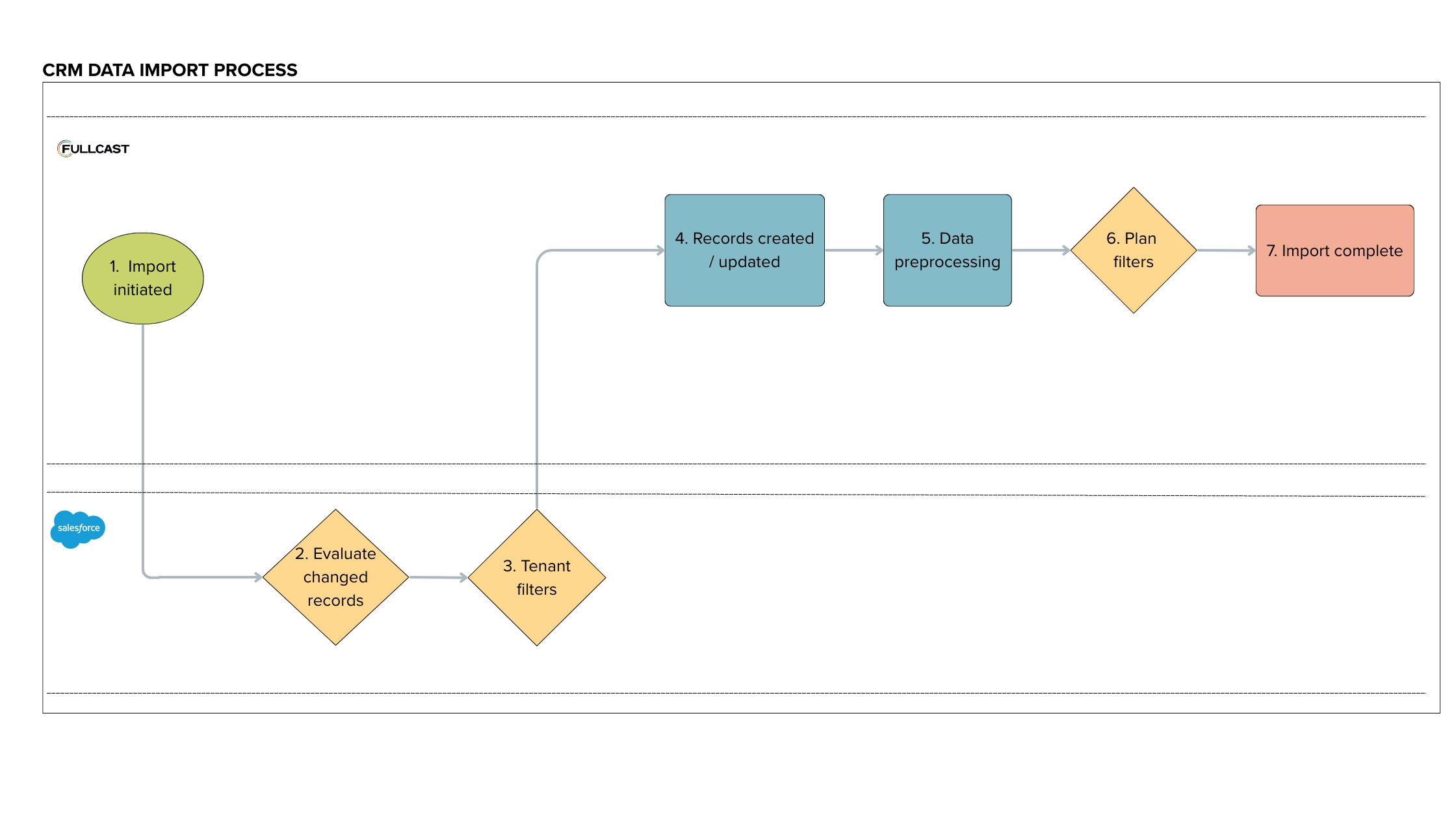
Import initiated: Imports are initiated from the Fullcast side. They can be initiated manually or on a schedule. Best practice is to schedule an import job at least once daily.
Evaluate changed records: For a “migrate latest” import job, Fullcast uses the
LastModifiedDatefield value to determine whether they have been changed since the last successful import. If theLastModifiedDateis more recent than the start date of the last successful import, then the record will be included in the “migrate latest” import job.Tenant filters: In cases where certain CRM records should never be imported into Fullcast, you may apply a tenant-level data filter. This filter is applied before records are brought into the Fullcast database.
Records created/updated: The set of records that are imported into the Fullcast database are those that have been changed and included after tenant filters processed.
Data preprocessing: After data is imported into Fullcast and before any rules are run, the system performs a series of data preprocessing steps to ensure data is standardized and consistent.
Plan filters: In addition to tenant filters, you may also create plan-level data filters. Note that plan-level data filters are not mutually exclusive; that is if records should exist only in one plan versus in multiple plans, you must carefully construct plan filters.
Import complete: When an import completes, the job status page will update accordingly.
Data preprocessing
Mapping and data normalization: The system processes geographic data fields by converting them into standardized formats. For example, various entries for a country such as "U.S.," "United States," or "America" are all normalized into a single, consistent code. This ensures consistency for hierarchies and mapping.
Note
The country field is critical for processing geographic data, as other location fields like city or postal code cannot be validated accurately without it.
Account family calculations: The system calculates parent-child relationships between accounts to determine the ultimate parent for each account based on the imported data. This hierarchy information is then stored in specific fields for use in various features.
Metrics calculation: The system calculates metrics before any rule processing. This ensures that aggregated data, including values from related objects, is ready for use in subsequent rule-based allocation.
Auto rerun rules
Auto rerun rules are an optional feature, which allows the system to automatically allocate records to hierarchy nodes automatically and immediately upon the conclusion of an import job.
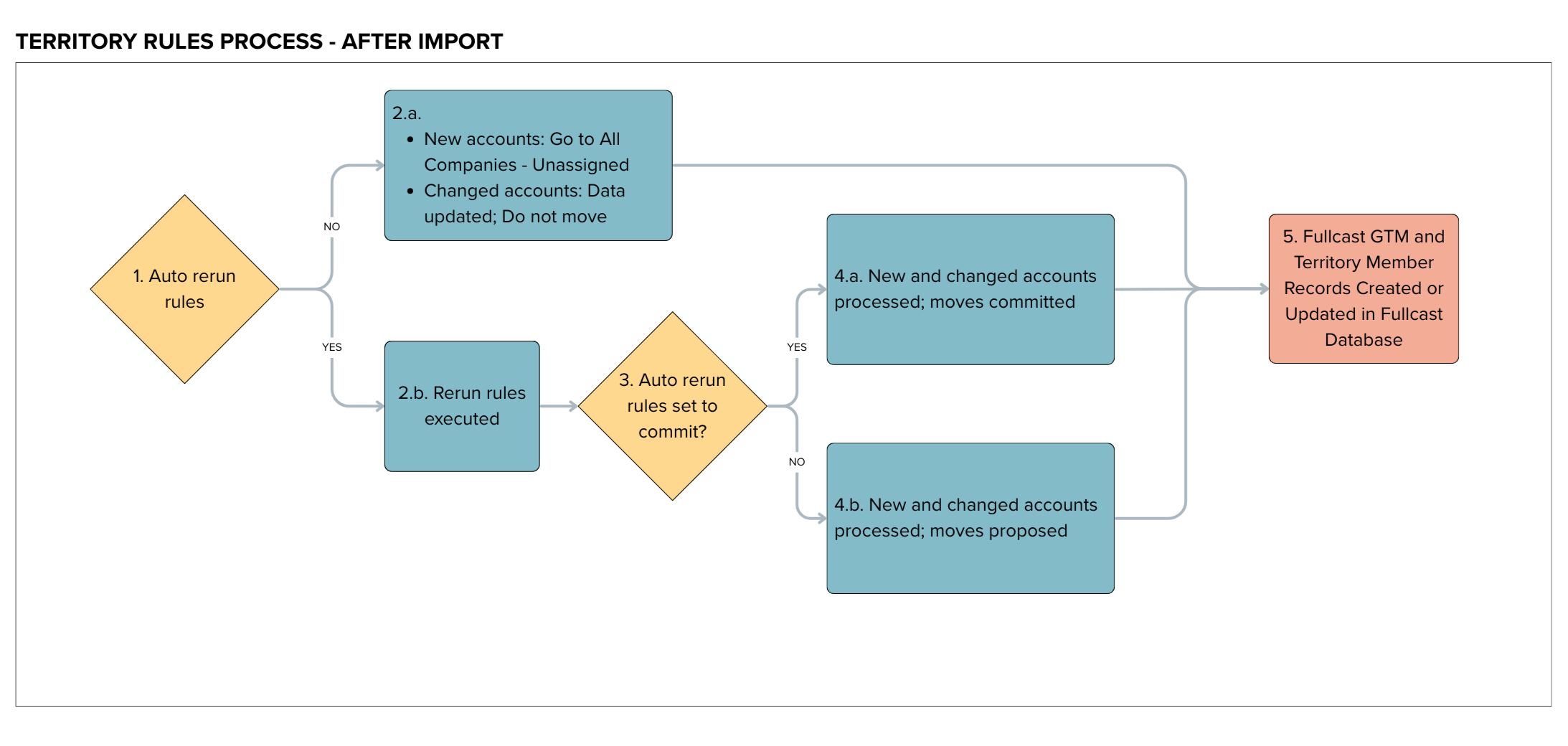
Without auto rerun rules
If auto rerun rules is not enabled:
All newly imported records are placed in the level 1 unassigned node. For example, accounts would be in All Companies - Unassigned.
Changed accounts will reflect their updated data in Fullcast, but they will not be automatically moved between plan hierarchy nodes.
The Fullcast GTM and Territory, Team, and Product Group Members are updated to reflect new records in the Fullcast database.
With auto rerun rules
When auto rerun rules is enabled, the system automatically processes hierarchy allocation for new and changed records. From there, the outcome of auto rerun rules is controlled by settings such as which records / nodes are configured for auto rerun rules and whether auto rerun rules is set to commit or propose.