Sales Manager needs to distribute the Leads, Opportunities, and Accounts evenly to all the available sales representatives. To achieve this, round-robin functionality is used in a scheduling algorithm that distributes leads/opportunities/accounts evenly among all available resources. This ensures that no single resource is overworked, which can lead to errors and other issues down the line.
Before you begin
Round robin is one of the Fullcast routing policy stages. As you configure this policy stage, review the details below to anticipate how the round-robin policy stage will process and distribute records. In addition to the basic functionality below, additional participant pools based on teams are also available in round-robin policies as of package 2.160.
How Round-Robin Functionality Works
The below flowchart explains how a simple round-robin functionality works.
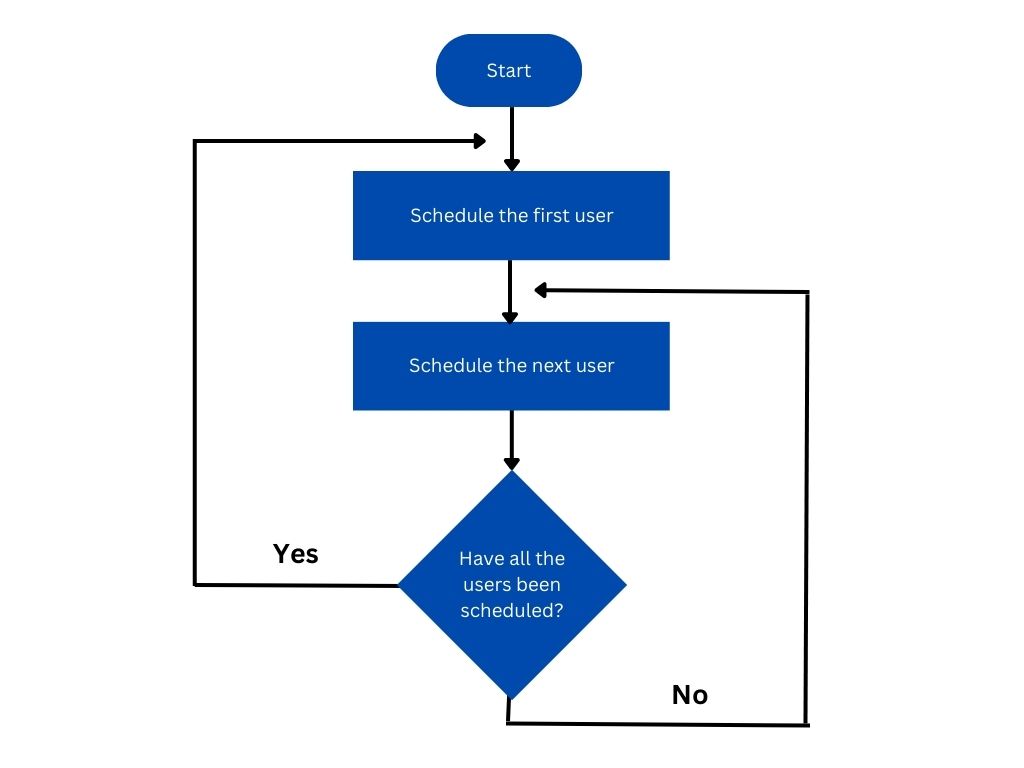
Figure 1. Round-Robin Flow Chart
Scenario 1
Let's consider there are four participants, John, Michael, Nicholas, and Kate in the round-robin list. 20 leads have to be distributed among these 4 sales representatives. According to the round-robin algorithm, the system will assign the leads in the following pattern.

Figure 2. Weightage
All the 20 Lead records will be distributed among these four members equally. But this is an ideal scenario. Fullcast takes into consideration many factors, before allotting the lead to the participant.
Fullcast's round-robin functionality
The factors considered while allotting participants in round-robin are:
Weightage: Sales Managers give different weightage to each sales representative according to their performance. The number of cases routed to the person depends on the weightage given to the person by the sales manager. If a person is given more value in the weightage column, then the person gets routed with more cases. If everyone gets the same value then every person gets an equal share of the leads.
Example: In the above example, John has 5 years of sales experience so the sales manager gives him a weightage score of 4. Michael joined the company 4 years ago and gets a weightage of 3. Nicholas has 2 years of experience so the sales manager gives him a weightage of 2. Kate is a new employee and in her training period so she is given a weightage score of 1. This means John, with the most experience, will handle the largest share of the workload, while Kate, who is still learning, will receive a smaller portion. The round-robin algorithm will assign the leads to the participants according to the weightage score. With the given weightage, the allotment will be like below:

Figure 3. Example Weightage
Skillset: If a participant is equipped with a skill that matches the skill required for the lead, then skills will be given priority while assigning that particular lead. The skill of the representative is given as an input value (inputVal2) in the routing flow.
Example: Imagine a lot of new leads are coming in from a French-speaking region. Nicholas is the only team member fluent in French. Therefore, when assigning these leads, language skills take priority. Leads 3, 7, 11, 14, 18, and 20, all from French-speaking regions, will be assigned directly to Nicholas.The remaining leads will then be distributed among the other team members based on their experience level (the weighting system mentioned earlier).

Figure 4. Example Weightage
Limits: The number of cases routed to a particular participant can be restricted using the Limits field. You can set a limit to any participant, on an hourly, daily, weekly, and total limit basis. Once the set limit is reached for the particular person the case gets routed to the next eligible person. The leads get assigned only till the limit reaches zero. We can start assigning the limits again when the particular time is reached and the limit is reset.
Example: Let'sconsider 10 leads have to be distributed among John, Michael, and Nicholas. The limit is set for each person and the distribution is as follows:

Figure 5. Example Distribution
Vacation: The vacation details of the person can also be managed while creating the policy by selecting the vacation start date and vacation end date from the corresponding columns. So when the participant is on vacation then the lead is assigned to the next eligible participant in the queue.
Status: Some participants may be available on the list but their status might be inactive. The status column helps us identify whether the particular person is active or inactive to handle the particular case. When the status of the person is inactive, the lead gets assigned to the next eligible participant.
Fullcast considers all the above five criteria to assign the lead/case/contact/account to the respective participant available in the round-robin queue.
How round-robin functionality with exceptions work?
The below flowchart explains how a round-robin functionality with exceptions works.
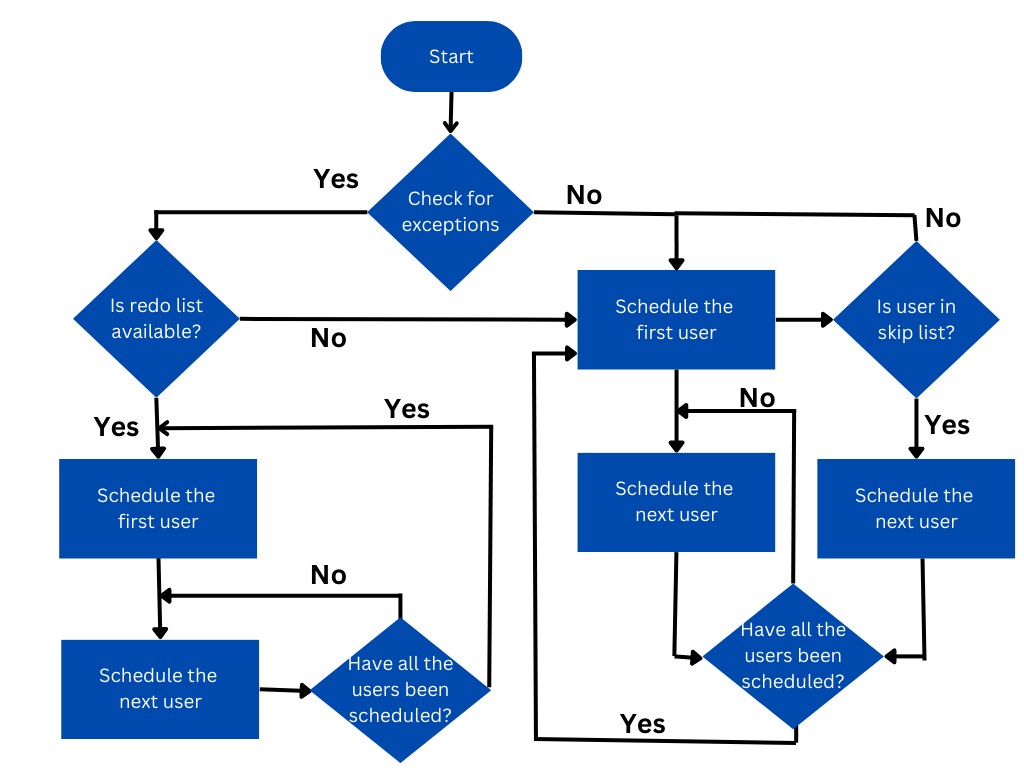
Figure 6. Round-Robin Flow Chart
Scenario 2
In the above scenario, lets consider, Michael is in redo list and Kate is in skip list. The algorithm will now first check who is there in the redo list. The lead 1 will now be assigned to the person who is there in the Redo list and his name will be removed from the redo list after allotment. So in this case, Lead 1 will go to Michael. Lead 2 will go to the usual round-robin queue and so it gets allotted to John and Lead 3 to Michael and Lead 4 to Nicholas and ideally lead 5 should go to Kate. But Kate name is listed in Skip list, so she should not be allotted any lead and after that her name will be removed from the skip list. Hence again the round-robin queue will continue and lead 5 will go to John again. So the distribution of work will be
Lead 1 - Michael (Since his name in redo list)
Lead 2 - John
Lead 3 - Michael
Lead 4 - Nicholas
Lead 5 - John (Since Kate name in Skip list)
Lead 6 - Michael
Lead 7 - Nicholas
Lead 8 - Kate (Since Kate name was removed from skip list after the skip)
Lead 9 - John ....... (and the queue continues till lead 20)

Figure 7. Example Weightage
Information:
For more information on managing exceptions in round-robin functionality, refer to the Manage Exceptions in Round-Robin article.