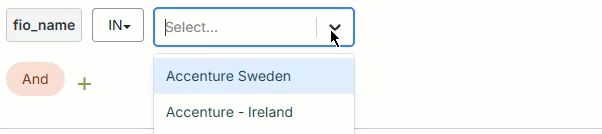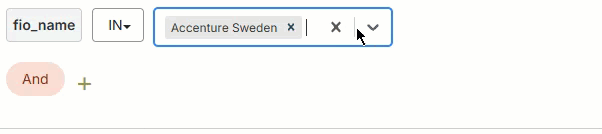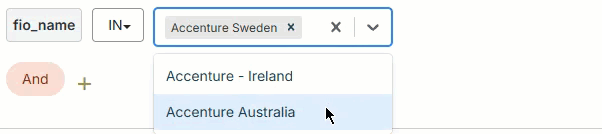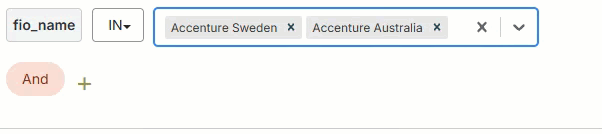
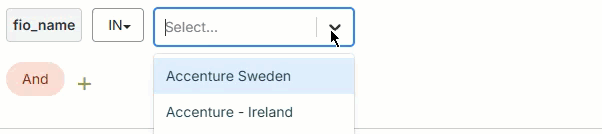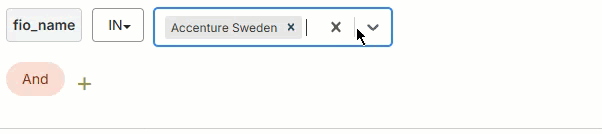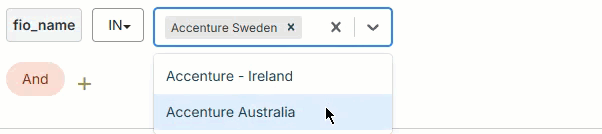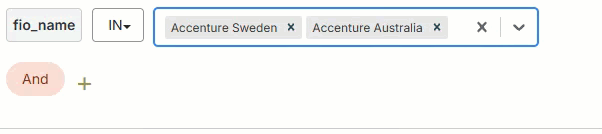
Use the filter builder in several areas of the Fullcast platform to include or exclude imported records at the plan level, add filters to bucket and smart plan rules, filter accounts in the account table, and more.
Filter builder functionality
.png)
Statement groups: Determines if all the conditions must be true (And) or at least one condition is true (Or).
Or: Any of the statements can be true.
And: All of the statements must be true.
Delete option: Removes that condition or operator from the filter.
Field selector: Specifies the field, variable, or data attribute that the filter rule evaluates.
Input value: The specific value compared against the field based on the selected operator.
Add option: Adds a condition or group of conditions to the filter.
Comparison operator: Defines how the selected field is compared to the input value.
Comparison operators
Each comparison operator determines how the field is evaluated against the input value and if that comparison meets the specified criteria to include or exclude the data. The following provides and description of each comparison operator.
Note
Availability of the comparison operators depends on where you use the filter builder in Fullcast and the field type. For example, the Account Name field uses string type comparison operators (contains, starts with) and Annual Revenue uses numeric type comparison operators (is greater than, is less than).
Equals to / equals
The field's value must match exactly the same as the input value.
Not equals to / Does not equal
The field's value must be anything other than the input value.
Contains
The field's value must include the input value as a substring anywhere within it.
Does not contain
The field's value must not include the input value anywhere within it.
Starts with
The field's value must begin with the input value.
Not starts with
The field's value must not begin with the input value.
Ends with
The field's value must end with the input value.
Is blank / is empty
The field must have no data entered in it (it is null or empty).
Is not blank / is not empty
The field must contain any value whatsoever.
Is any of
The field's value must match one of the input values.
To add values:
Click on the input value field.
Type a value.
Press
Enter.Repeat to add more values as needed.
Is none of
The field's value must not match any of the input values.
To add values:
Click on the input value field.
Type a value.
Press
Enter.Repeat to add more values as needed.
Between / is between
Considers the numbers between and including the input values. For example, if the values are between 1 - 100, it would consider all numbers between the given values including 1 and 100.
In
The field's value must include one of the input values. The input value field for the In operator may be a text field where you type multiple values manually or a picklist where you select multiple values from a dropdown.
To add values with the text field:
Click on the input value field.
Type a value.
Press
Enter.Repeat to add more values as needed.
To add values with the picklist:
Click on the dropdown arrow in the input value field.
Select the value from the dropdown
Repeat to add more values as needed.
Less than / is less than
The field’s value must be less than the input value.
Greater than / is greater than
The field’s value must be more than the input value.
Less than or equals / is less than or equal to
The field’s value must be less than or equal to the input value.
Greater than or equal / is greater than or equal to
The field’s value must be more than or equal to the input value.
Input value types
The input value depends on the field type you select. The following lists the available input value types
String
Type a sequence of characters (letters, numbers, symbols, and spaces) that forms a text value.
Boolean
Select true or false from the dropdown.
Date
Select the calendar day, month, and year from the interactive calendar.
Click on the input value field.
Click the dropdown arrow.
Select the date.
Note
You can use the arrows or click on the date header to drill down and select the year, month, then day.
Click Ok.
Press
Enter.
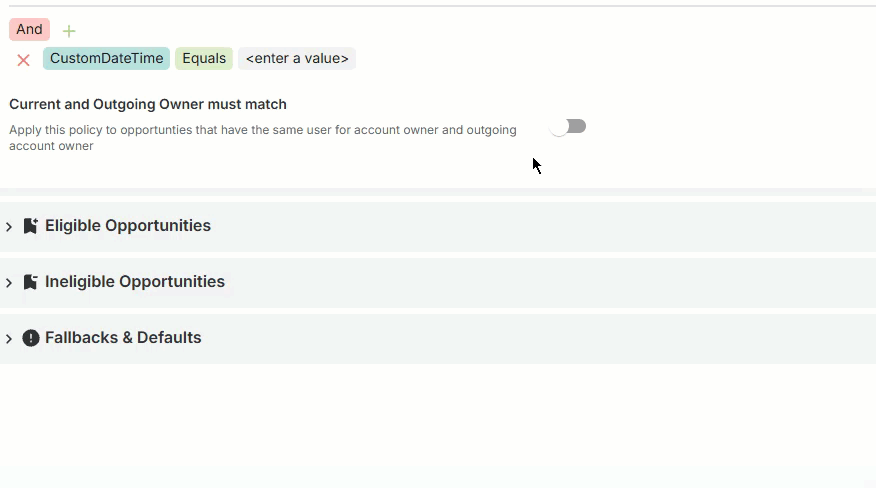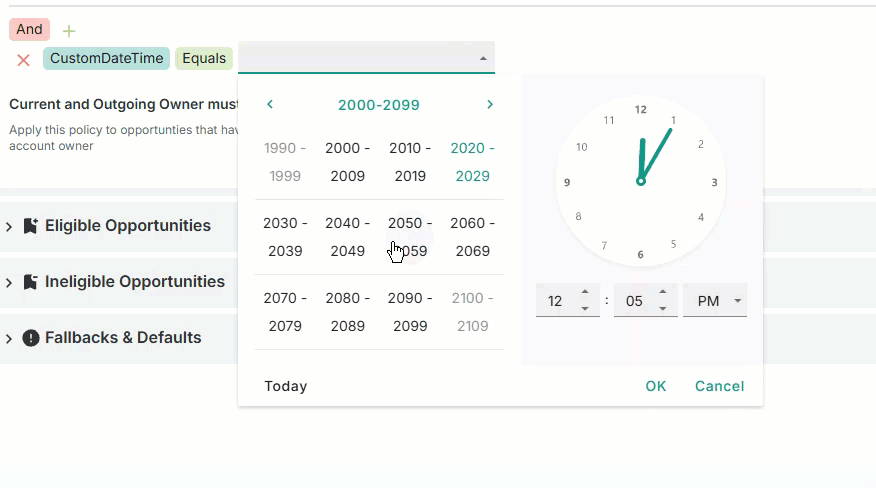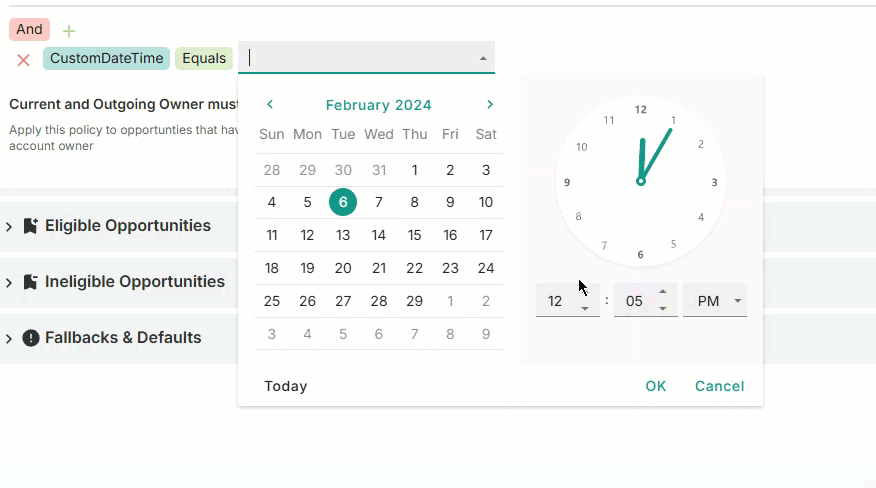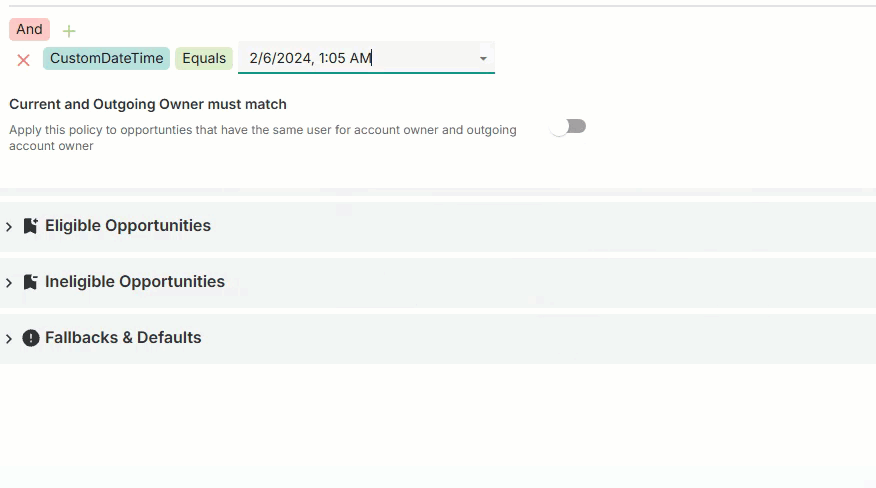
Date and time
Select the calendar day, month, year, and time from the interactive calendar and clock.
Click on the input value field.
Click the dropdown arrow.
Select the date.
Note
You can use the arrows or click on the date header to drill down and select the year, month, then day.
From the clock fields, select the time.
Click Ok.
Press
Enter.
Integer
Type a whole number (no decimal or fraction).
Picklist
Select multiple options from the dropdown.
Filter builder criterion best practices
When you use the filter builder, create filters in the simplest way possible to include or exclude the required data. Determine whether to start your criteria with the And or the Or condition, and how to group conditions.
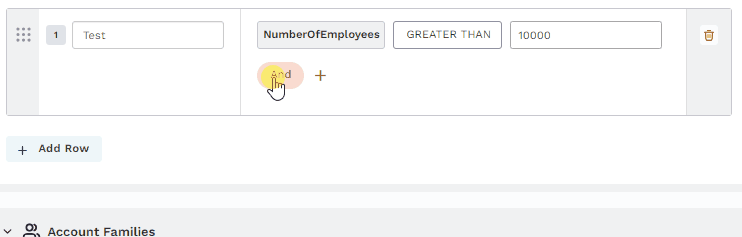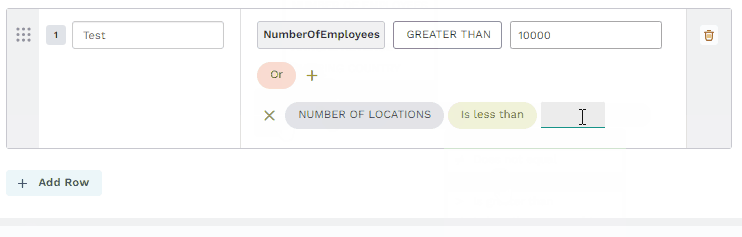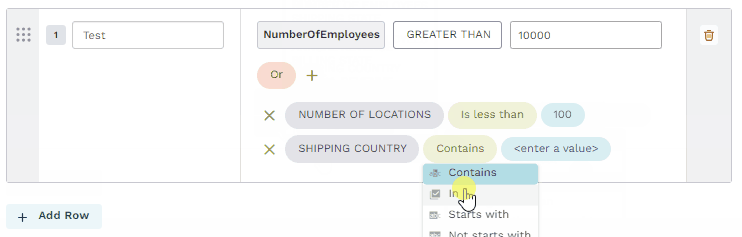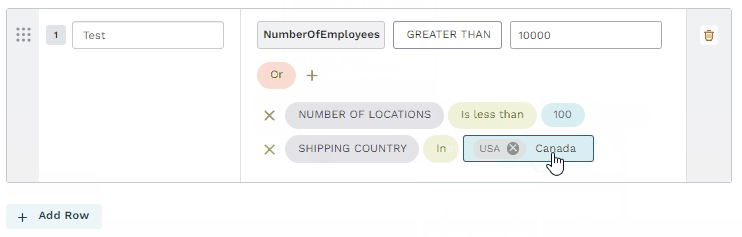
Create hybrid filters
Many criterion require hybrid filters that combine Or conditions that group And criterion. Each group is compared and includes or excludes data if any of the group of And conditions are met. Refer to a group of three conditions or a group of two conditions in the following examples.
Add an
Andcondition at the highest level for every multi-filter group so that eachAndfilter stays together.With multiple groups, set the first criteria to a false criteria and the first operator as
Or. This makes all accounts that fall past the initialOrand the remaining logic levels easier to organize.If you use more than one range of values on the same field in a single bucket, put the largest range number first.
Filter criteria examples
The following are common examples of filters built for different use cases.
Territory filter criteria examples
Break up segments according to the size of the company and other related criteria.
A single condition or a group of two conditions
Qualify an account to be in the Enterprise segment based on the number of employees and industry.
Criteria setup:
NumberOfEmployees greater than 20000
Or
And
Number of Employees is greater than 10000
Industry does not equal Healthcare

Result: The larger employee count (20,000) is evaluated first to find matches then the second condition in addition to the industry is evaluated to allocate accounts. If you put Number of Employees greater than 10,000 first, there would be no accounts between 10,000 and 20,000 left to allocate.
A group of three conditions or a group of two conditions
Qualify an account to be allocated in the Mid Market segment based number of employees, annual revenue, and customer fit score.
Criteria setup:
NumberOfEmployees EQUALS TO 1.2
Or
And
Number of employees is greater than 15000
Annual Revenue is greater than 10000000
Customer Fit Score is between 5 - 8
And
Number of employees is between 1000 - 15000
Customer Fit Score is greater than 8

Result: When you set the first condition to something that is always false (number of employees equals to 1.2), both of the other criteria groups, which have multiple conditions, are evaluated together.
A group of two conditions
One group of conditions that qualify an account as an SMB account.
Number of Employees less than 1000
And
Parent Name is blank

Result: Finds all accounts with less than 1000 employees there is no parent account.
A dummy condition to manually create a territory for named accounts
When you have a territory that needs to be in the same level as certain segments, but it will contain only named accounts. Use a condition that will always be false to create an empty bucket, then manually move accounts to this bucket and mark them as named accounts.
Note
Only use this method to create a subset of territories that consist only of named accounts.

Two groups of conditions OR one single condition
Create three criteria that can qualify an account to be in the Enterprise segment.
And
NumberOfEmployees is greater than 10000
Bookings potential is greater than 10000000
Or
And
Bookings potential is greater than 1000000
Customer Fit Score is greater than 1000000000
Or
Bookings potential is greater than 2000000